-
Review
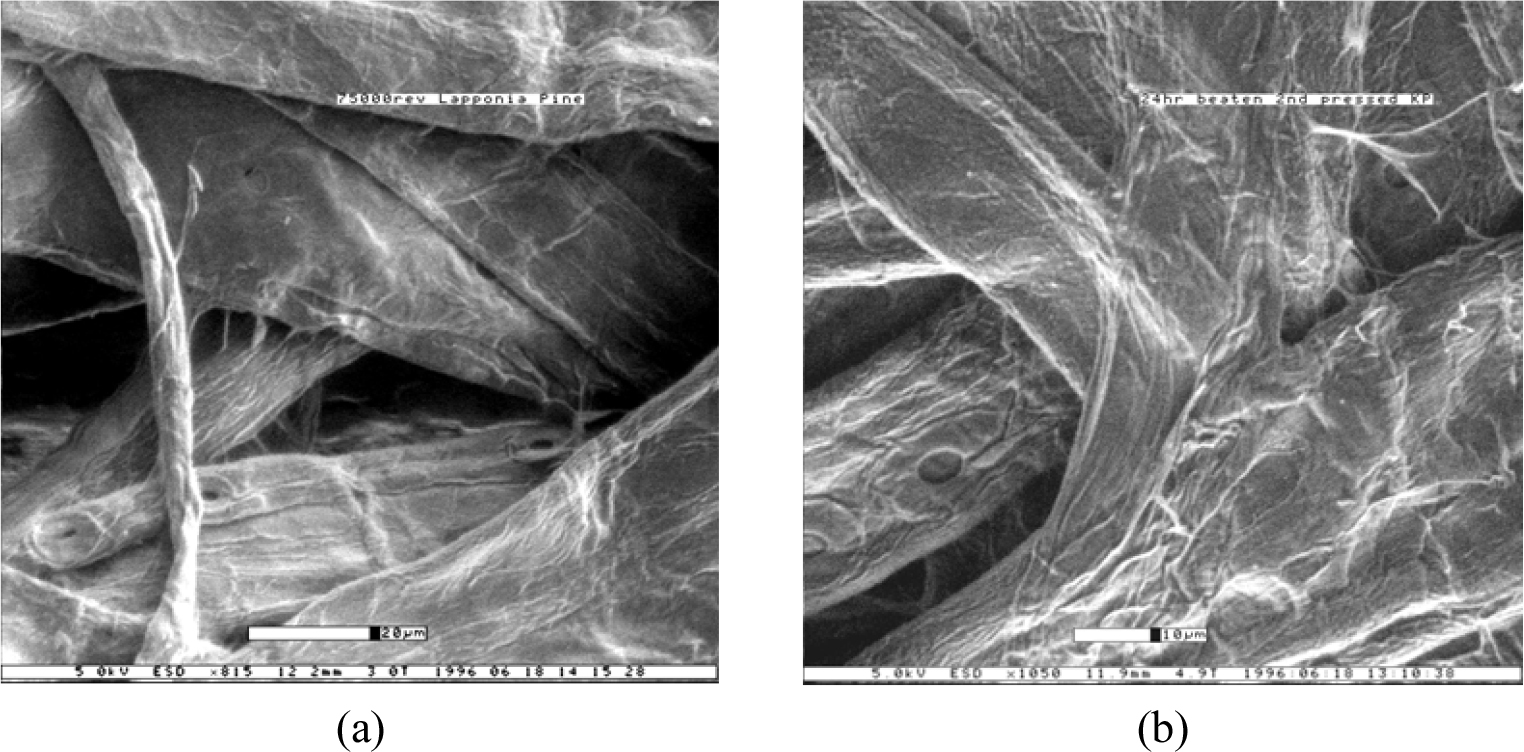
- Navigating the Energy-Quality Trade-Off of Refining Process in Stock Preparation: Fundamentals, Mechanisms, and Technological Advances in Refining (Part I)
- Chul-Hwan Kim
- Refining is a critical, energy-intensive process that fundamentally determines fiber properties and paper quality. This review—the first in a two-part series—establishes a …
- Refining is a critical, energy-intensive process that fundamentally determines fiber properties and paper quality. This review—the first in a two-part series—establishes a technical foundation for understanding refining mechanisms, equipment configurations, and plate technologies. It analyzes the mechanical transformation of wood fibers through fibrillation and shortening, focusing on how refiner geometry and the four-stage treatment cycle (capture, impact, compression, and relaxation) govern freeness and strength development. Key advancements are highlighted, including vertical bar designs and high-performance alloys that extend service life by 30–50% while improving energy efficiency. By correlating plate engineering with morphological changes via SEM microscopy, this work provides the groundwork for Part II’s focus on refining theories and operational optimization to resolve the energy-quality paradox. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper

- Brand Design: Research on the Color Management of Printed Images on Tea Paper Packaging
- Xiaying Liu
- In this paper, we briefly investigate the management of color in patterns printed on paper packaging. We used a back-propagation neural network …
- In this paper, we briefly investigate the management of color in patterns printed on paper packaging. We used a back-propagation neural network (BPNN) algorithm, improved by using a genetic algorithm (GA), to convert the pattern colors from CIELAB color space to CMYK color space, thus enabling their reproduction and printing using printing equipment. We performed simulation experiments in which we compared the results from the polynomial-regression algorithm and the Neugebauer algorithm. We also evaluated the printing of the pattern designed in this paper and found that the patterns printed using the GA-BPNN algorithm had smaller color differences and were more stable. For the tea-packaging pattern designed in this paper, the color differences in printing that utilized the GA-BPNN algorithm were the smallest, as they were also in manual scoring. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
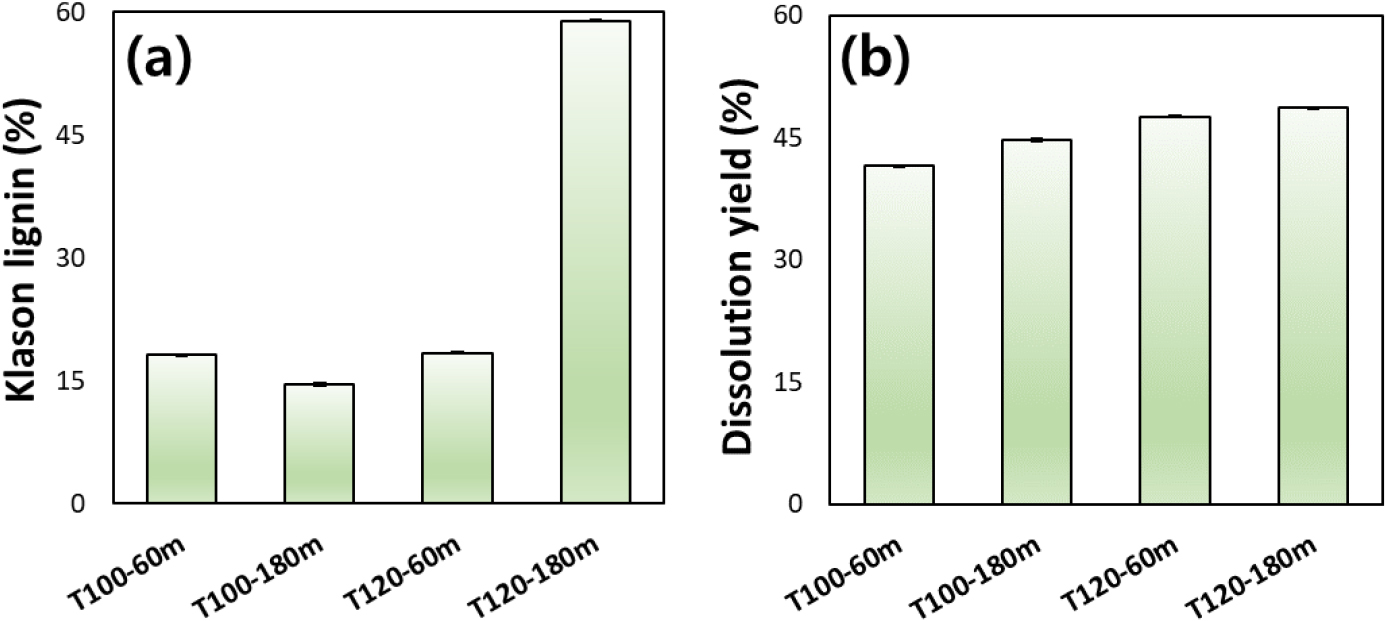
- Effect of Pulping Condition on Bamboo Pulp Properties in Glycol Ether-Based Organosolv Process
- Sa Rang Choi, Jiae Ryu, Jung Myoung Lee
- The increasing demand for sustainable materials has intensified interest in alternative strategies for non-wood biomass such as bamboo. In this study, a …
- The increasing demand for sustainable materials has intensified interest in alternative strategies for non-wood biomass such as bamboo. In this study, a glycol ether-based organosolv pulping process was investigated to evaluate the influence of reaction conditions and pulping liquor composition on the properties of bamboo pulp. The results showed that this led to significant screened yield loss and the production of fines (>0.2 mm) under excessively harsh conditions. Mild temperature conditions (100°C) preserved fiber length and strength, resulting in improved papermaking performance. The dissolution yield increased with increasing reaction temperature, reaction time, and chemical severity (Glycol ether ≥ 95% and catalyst ≥ 0.6 M), indicating that such conditions are suitable for fabricating dissolution-grade bamboo pulp. Based on these results, it is confirmed that the properties of bamboo pulp can be effectively adjusted by controlling both the reaction conditions and the composition of the pulping liquor. The glycol ether-based organosolv pulping process provides fundamental data for selectively producing either paper-grade or dissolution-grade bamboo pulp, depending on the targeted end use. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
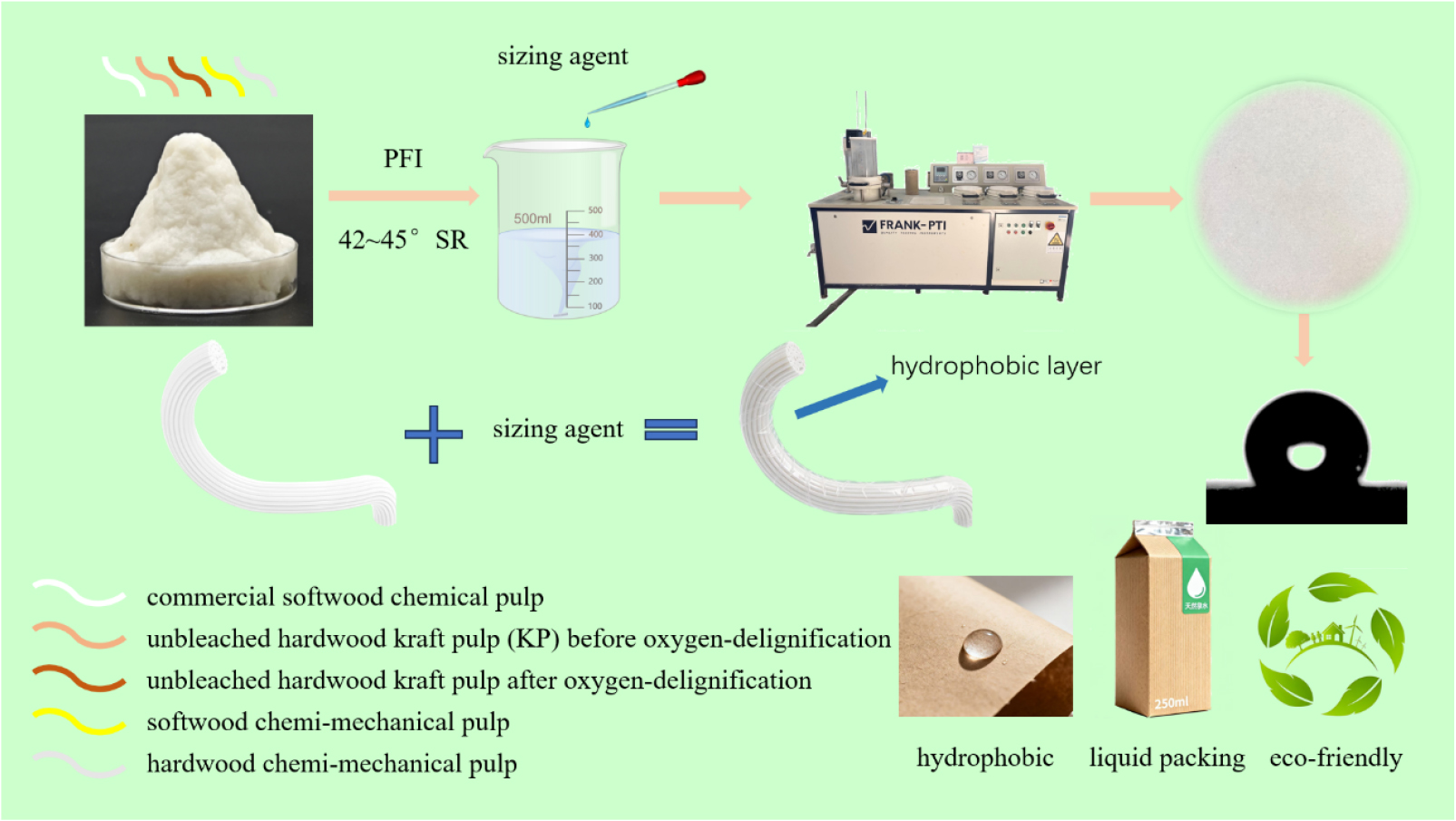
- Influence of Sizing Treatment on the Hydrophobicity and Strength Properties of Cellulose-Based Paper Materials for Liquid Packaging
- Hao Liu, Guihua Yang, Ming He, Shaoguang Wang, Qimeng Jiang, Chenyue Yu, Jiachuan Chen
- The non-biodegradable petroleum-based plastic packaging materials have caused pollution to the human living environment. With the implementation of global plastic ban, the …
- The non-biodegradable petroleum-based plastic packaging materials have caused pollution to the human living environment. With the implementation of global plastic ban, the research of cellulose-based paper materials as alternative to plastic for liquid packaging have become a key focus. In this work the effects of sizing treatment on the hydrophobicity and strength of cellulose-based paper materials for liquid packaging was investigated. The sizing process parameters were optimized based on the strength properties, water absorption Cobb value and hydrophobicity contact angle of the cellulose-based paper materials after sizing treatment. The results indicated that the single alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) sizing exhibited optimal hydrophobic performance compared to the single rosin sizing. The cellulose-based paper materials obtained the enhancement of hydrophobicity when the AKD dosage was 1.5 wt% (based on oven-dry pulp fiber), with a minimum Cobb value of 21.9 g/m2 and a maximum contact angle of 118.6°. For the mixed sizing of rosin/AKD, a decrease of the mass ratio of rosin is beneficial to improve the hydrophobicity of the paper materials, and the optimal strength and hydrophobicity were achieved at mass ratio of rosin 30% : AKD 70% in the mixed sizing process, with a tensile strength of 7.62 KN/m, a bursting strength of 491.2 kPa, a tearing strength of 220 mN, a Cobb value of 20.0 g/m2 and a contact angle of 121.2°. Furthermore, the sequence of adding rosin and AKD in the mixed sizing process had no influence on the performance of the cellulose-based paper materials. It is expected that a theoretical reference for the development of high-performance cellulose-based liquid packaging materials will be provided. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
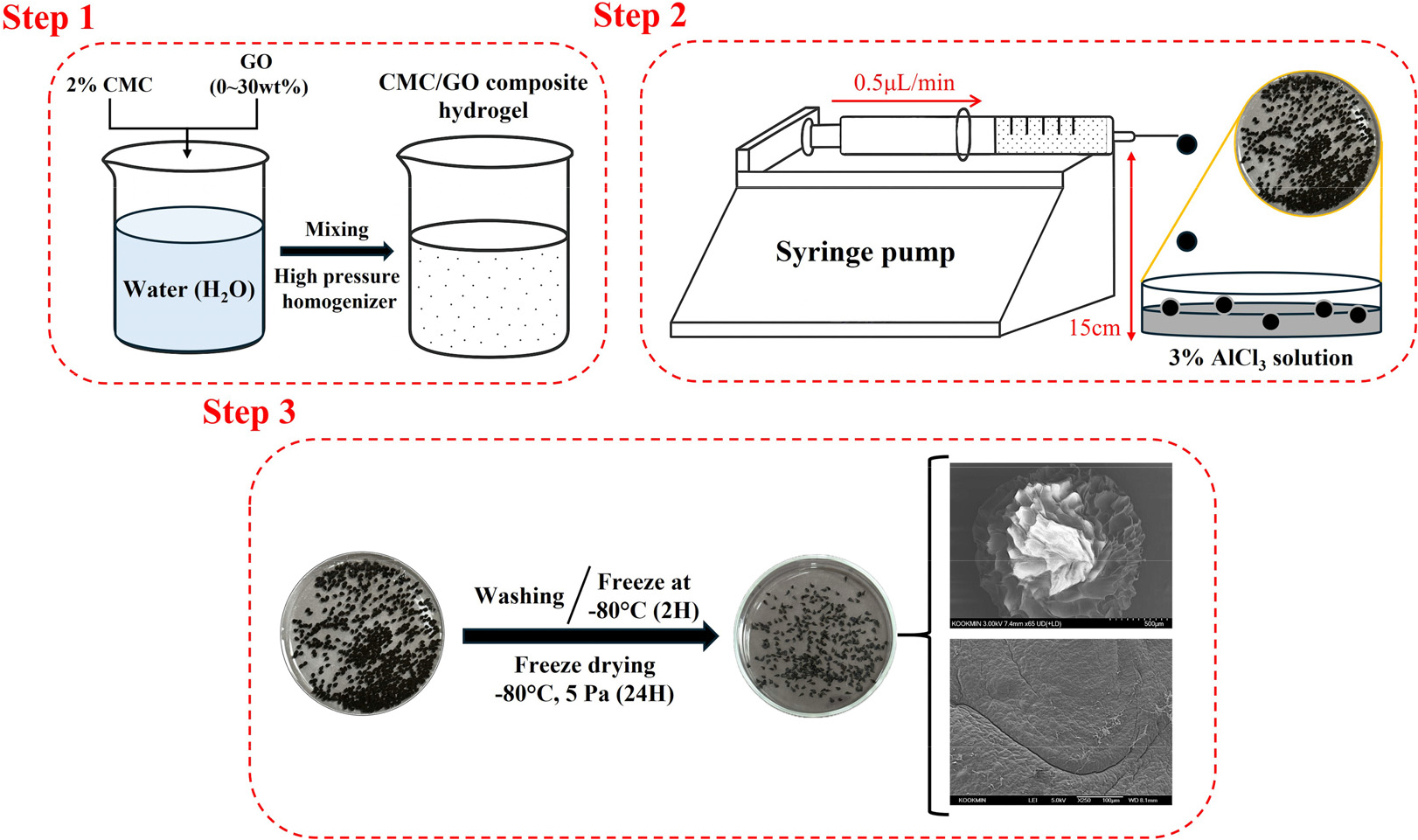
-
Fabrication of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Graphene Oxide Composite Beads and Evaluation of Their Adsorption Behavior for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions
수용액 내 메틸렌블루 제거를 위한 카르복시메틸셀룰로오스/그래핀옥사이드 복합 비즈 제조 및 흡착 거동 평가
-
Jae-Young Kim, Soon Wan Kweon, Dae-Hyun Jang, Hyoung Jin Kim, Jae Ho Ryu, Tai Ju Lee
김재영, 권순완, 장대현, 김형진, 류재호, 이태주
- Synthetic dyes in industrial effluents are major environmental contaminants due to their high toxicity and resistance to biodegradation, posing serious risks to …
- Synthetic dyes in industrial effluents are major environmental contaminants due to their high toxicity and resistance to biodegradation, posing serious risks to aquatic ecosystems and human health. In this study, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/graphene oxide (GO) composite beads were fabricated via ionic crosslinking in an Al3+ solution by freeze-drying, and their performance for removing cationic methylene blue (MB) was systematically evaluated. The physicochemical properties of the beads were characterized using rheometry, FT-IR spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The influence of GO content on MB removal performance was assessed through adsorption isotherms and kinetic studies. All samples exhibited adsorption behaviors well described by the Freundlich isotherm (R2 > 0.95), indicating heterogeneous surface adsorption sites and partial multilayer adsorption. Among the composites, the bead containing 20 wt% GO (GO20) showed the highest affinity and adsorption capacity (KF = 18.02). The adsorption kinetics were well fitted by the pseudo-second-order model (R2 > 0.94), with a calculated equilibrium capacity of qe = 71.4 mg/g, confirming that GO20 provides an optimal balance of rheological stability, structural integrity, and adsorption efficiency. These results demonstrate that CMC/GO composite beads are promising and sustainable adsorbents for the purification of dye-contaminated wastewater. - COLLAPSE
-
Fabrication of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Graphene Oxide Composite Beads and Evaluation of Their Adsorption Behavior for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions
-
Original Paper
-
Nanofibrillation of White Water Solids and Their Application to Papermaking Process
백수 고형분의 나노피브릴화 및 이의 제지공정 적용
-
Seung-wook Park, Kunhee Lee, Hakmyoung Lee, Hye Jung Youn
박승욱, 이건희, 이학명, 윤혜정
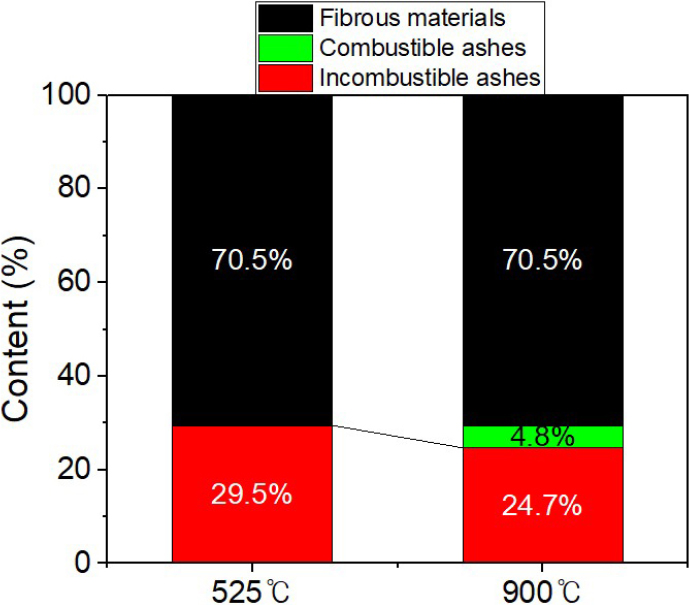
- This study investigated the valorization of white water solids generated during corrugating medium production by converting them into nanofibrils and applying them …
- This study investigated the valorization of white water solids generated during corrugating medium production by converting them into nanofibrils and applying them as strengthening agent and surface sizing additive in the papermaking process. Saveall-recovered solids were used as white water solids, and their composition and fiber morphology were analyzed. Through mechanical grinding, white water originated cellulose nanofibrils (WCNF), which consisted of nanofibril-inorganic matter composites, were produced. The applicability of WCNF as strengthening agent was examined while varying WCNF dosage and retention aid addition. Even without a retention aid, WCNF addition led to moderate increases in tensile, burst, and compressive strength because nanofibrils contributed to inter-fiber bonding. When a retention aid was added, WCNF was retained more effectively within the sheet, enabling the nanofibrils to fully reinforce the fiber network. Under these conditions, handsheets containing 5 or 7 wt% WCNF exhibited increases of approximately 20 to 26% in tensile, burst, and compressive strength and in bending stiffness compared with the handsheet without WCNF. WCNF was also incorporated into oxidized starch-based surface sizing formulations, leading to improved mechanical strength. These results demonstrate that nanofibrillated white water solids can be converted into high value functional materials capable of reinforcing fiber networks and improving the properties. The approach offers an effective strategy for upgrading papermaking by-products, enabling material circularity and potential reductions in raw material consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. - COLLAPSE
-
Nanofibrillation of White Water Solids and Their Application to Papermaking Process
-
Original Paper
-
Dual-Functional Lignin via Amination and Oxypropylation for High-Strength Hydrogels with Enhanced Network Integrity
아민화 및 옥시프로필화를 통한 이중 기능화 리그닌 기반 고강도 하이드로겔의 네트워크 안정성 향상
-
Min Soo Kim, Ji Won Heo, Yong Sik Kim
김민수, 허지원, 김용식
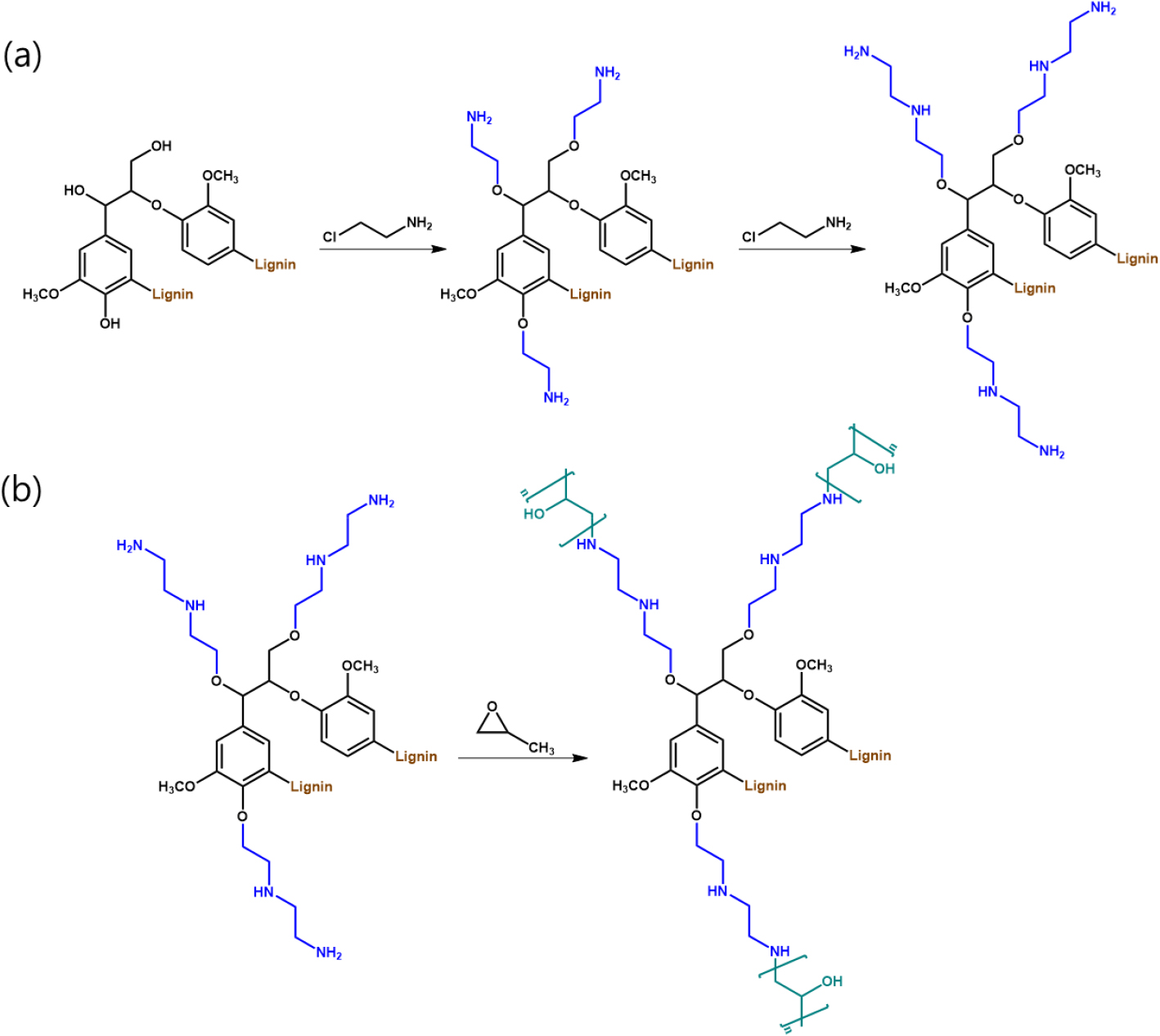
- In this study, lignin was sequentially modified via amination and oxypropylation to produce a dual-functional lignin derivative, and high-strength hydrogels were fabricated …
- In this study, lignin was sequentially modified via amination and oxypropylation to produce a dual-functional lignin derivative, and high-strength hydrogels were fabricated using the resulting lignin as a building block. It confirmed the introduction of amine groups and oxypropyl side chains, while molecular-weight analysis showed a pronounced increase in oxypropylated lignin (OL) compared with kraft lignin (KL), indicating successful structural expansion. The lignin-based hydrogels exhibited porous microstructures, and effective network formation via a ring-opening crosslinking reaction was verified. Notably, hydrogels prepared with dual-functional lignin displayed enhanced network integrity and significantly improved mechanical strength and durability relative to the reference system. These improvements were attributed to the synergistic effects of amine-derived reactive/interactive sites serving as network junctions and flexible oxypropyl side chains promoting compatibility, chain rearrangement, and energy dissipation. Overall, this work presents a practical sequential functionalization strategy to convert lignin into a hydrogel-active building block for sustainable, mechanically robust polymer networks. - COLLAPSE
-
Dual-Functional Lignin via Amination and Oxypropylation for High-Strength Hydrogels with Enhanced Network Integrity
-
Original Paper
-
Effect of Drying Temperature on Network Structural and Absorption-Retention Properties of CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers
건조 온도가 CMC/전분-기반 고흡수성 소재의 네트워크 구조 및 흡수·보수 특성에 미치는 영향
-
Ha-Neul Kim, Byoung-Uk Cho
김하늘, 조병욱
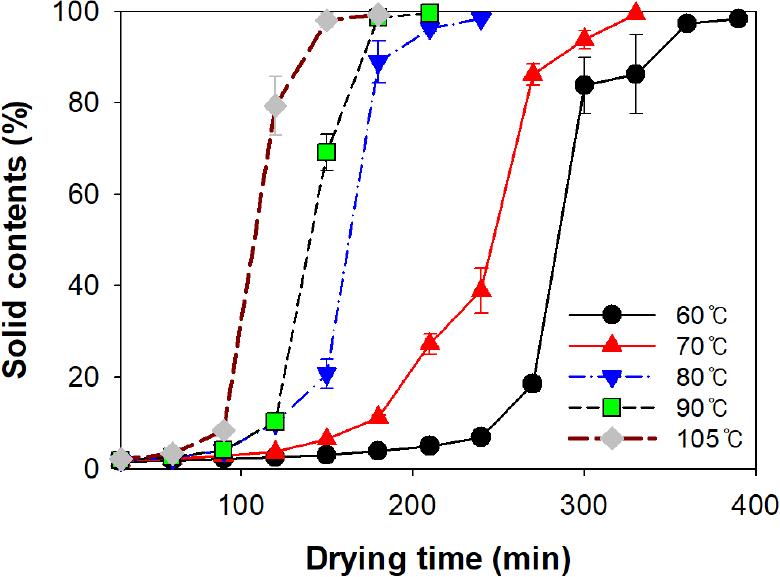
- Superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) were synthesized from carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and cationic starch via a mold-drying process, and the effect of drying temperature …
- Superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) were synthesized from carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and cationic starch via a mold-drying process, and the effect of drying temperature on their microstructure and hydrogel properties was systematically investigated. Aqueous CMC/starch solutions (1.5 wt%) were dried at temperatures ranging from 60 to 105°C and subsequently ground into powders. Increasing the drying temperatures significantly accelerated moisture removal, resulting in a marked reduction in drying time. SEM observations revealed dense polymer matrices without distinct open pores, while lower drying temperatures promoted layered structures due to gradual solvent evaporation. SAPs dried at lower temperatures exhibited higher free swelling capacity in both distilled and saline water. In contrast, higher drying temperatures led to reduced swelling but enhanced gel fraction, centrifuge retention capacity, and elastic-dominated viscoelastic behavior. These results demonstrate a clear trade-off between free swelling and gel stability governed by drying temperature, highlighting it as a key processing parameter for tailoring CMC/starch-based SAPs for specific applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Effect of Drying Temperature on Network Structural and Absorption-Retention Properties of CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers
-
Original Paper
-
Enhancement of Saline Absorbency in CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers by Incorporation of Sodium Bicarbonate
중탄산나트륨 첨가에 따른 CMC/전분 기반 고흡수성 고분자의 염수 흡수 특성 향상
-
Chan Hee Shin, Young Lae Kim, Byoung-Uk Cho
신찬희, 김영래, 조병욱
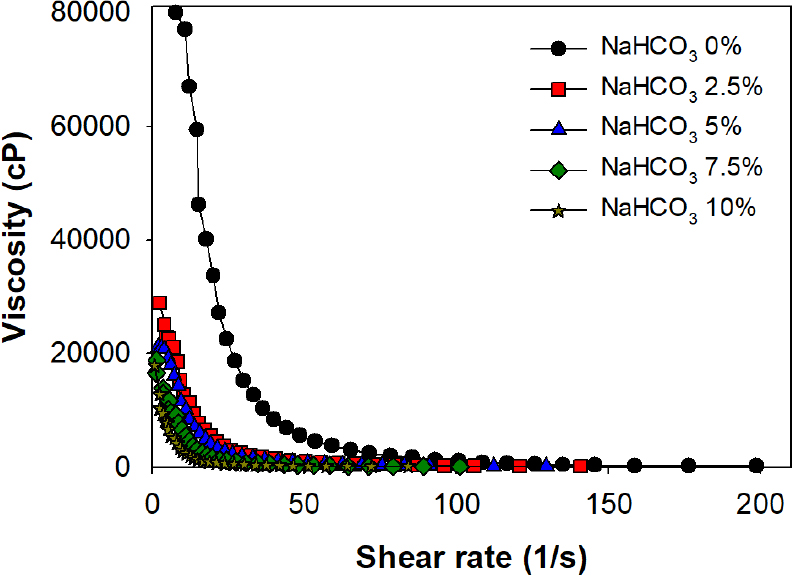
- Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/cationic starch (CS)-based superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) were prepared with different sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) contents to improve saline absorption …
- Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/cationic starch (CS)-based superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) were prepared with different sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) contents to improve saline absorption behavior while maintaining structural stability. The effects of NaHCO3 addition on network structure, swelling behavior, rheological properties, and mechanical stability under load were systematically investigated. A small amount of NaHCO3 (2.5 wt% on CMC and CS) significantly enhanced saline absorption, which was attributed to partial relaxation of electrostatic interactions between CMC and cationic starch and the formation of additional diffusion pathways. SEM analysis revealed the development of internal porous structures induced by weak foaming associated with CO2 generation during drying. However, increasing NaHCO3 content led to a reduction in gel strength, gel fraction, absorption under load (AUL), and centrifuge retention capacity (CRC) due to decreased effective crosslink density. These results demonstrate that controlled NaHCO3 addition provides an effective strategy to balance saline absorption performance and mechanical stability in eco-friendly polysaccharide-based SAPs. - COLLAPSE
-
Enhancement of Saline Absorbency in CMC/Starch-Based Superabsorbent Polymers by Incorporation of Sodium Bicarbonate



 Journal of Korea TAPPI
Journal of Korea TAPPI







