-
Review
- Properties, Preparation, and Applications of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels
- Tai Ju Lee, Hyung Won Lee, Hyoung Jin Kim
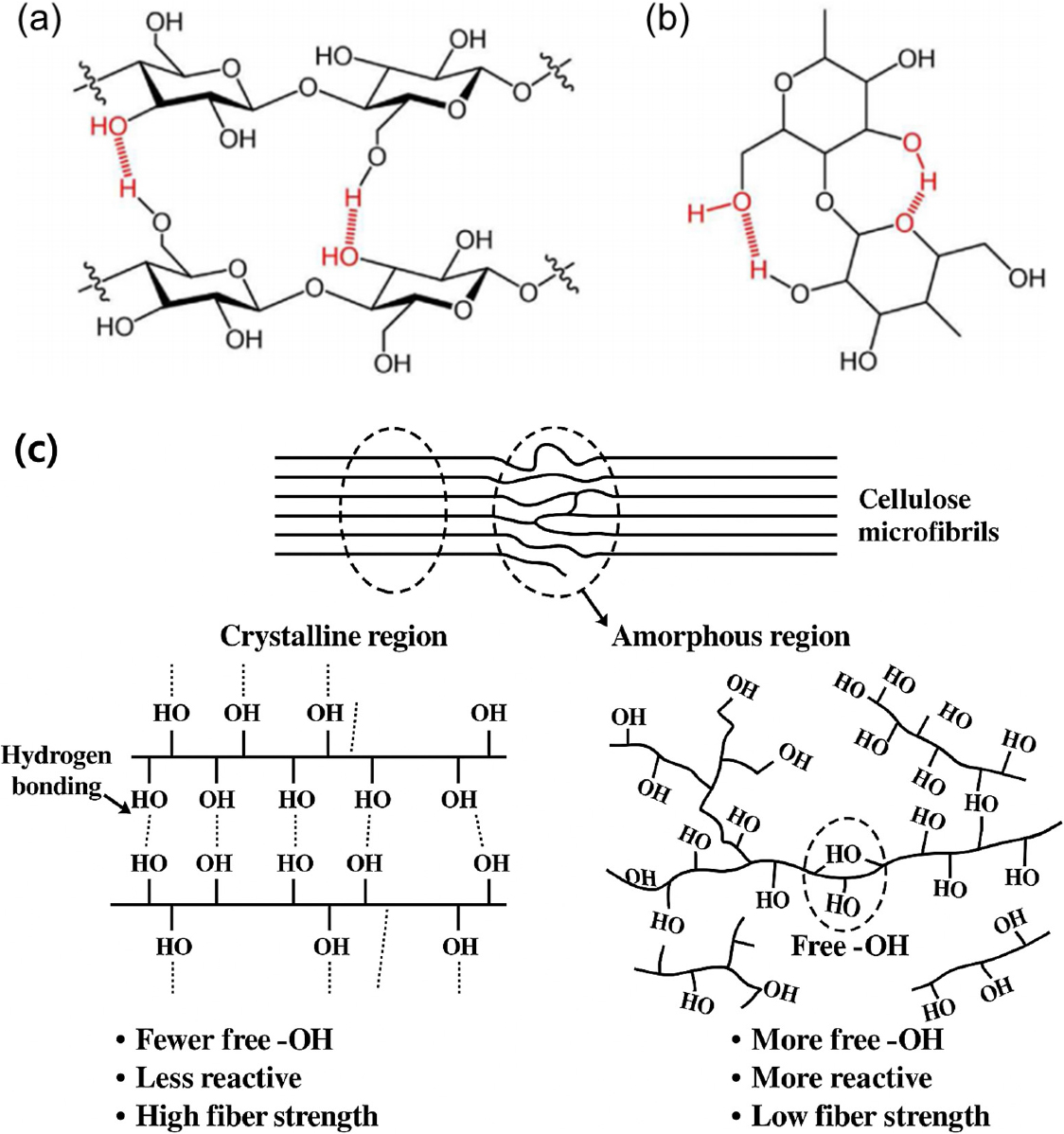
- Cellulose, a sustainable and versatile material, has attracted considerable attention owing to its eco-friendly properties and excellent physicochemical characteristics. Among various cellulose-based …
- Cellulose, a sustainable and versatile material, has attracted considerable attention owing to its eco-friendly properties and excellent physicochemical characteristics. Among various cellulose-based materials, hydrogels exhibit exceptional water retention capability, mechanical stability, and tunability, rendering them highly suitable for smart packaging, biomedicine, environmental remediation, sensing, and electronic applications. This review analyzes in depth the synthesis strategies, structural properties, and key applications of cellulose-based hydrogels. In smart packaging applications, cellulose-based hydrogels serve as active packaging materials that respond to environmental changes, enabling food preservation and freshness monitoring. In biomedicine, cellulose-based hydrogels show substantial promise for drug delivery, wound healing, and tissue engineering applications owing to their biocompatibility and tunable degradation. Their role in environmental remediation, including wastewater treatment and pollutant adsorption, further underscores their contribution to sustainability efforts. The integration of cellulose-based hydrogels into flexible, lightweight sensors and electronic materials has driven the development of advanced functional devices. With ongoing research and commercialization, these hydrogels are poised to become pivotal materials for sustainable technologies. Future advancements should focus on the optimization of synthesis techniques, improvement of mechanical properties while maintaining biodegradability, and enhancement of production scalability to advance green technologies and next-generation functional materials. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Global Warming Impact of Biomass Sawdust from Gamal (Gliricidia sepium) Production in Indonesia
- Citasari Hendrasetiafitri, Bramasto Nugroho, Dede Hermawan, Tatang Tiryana
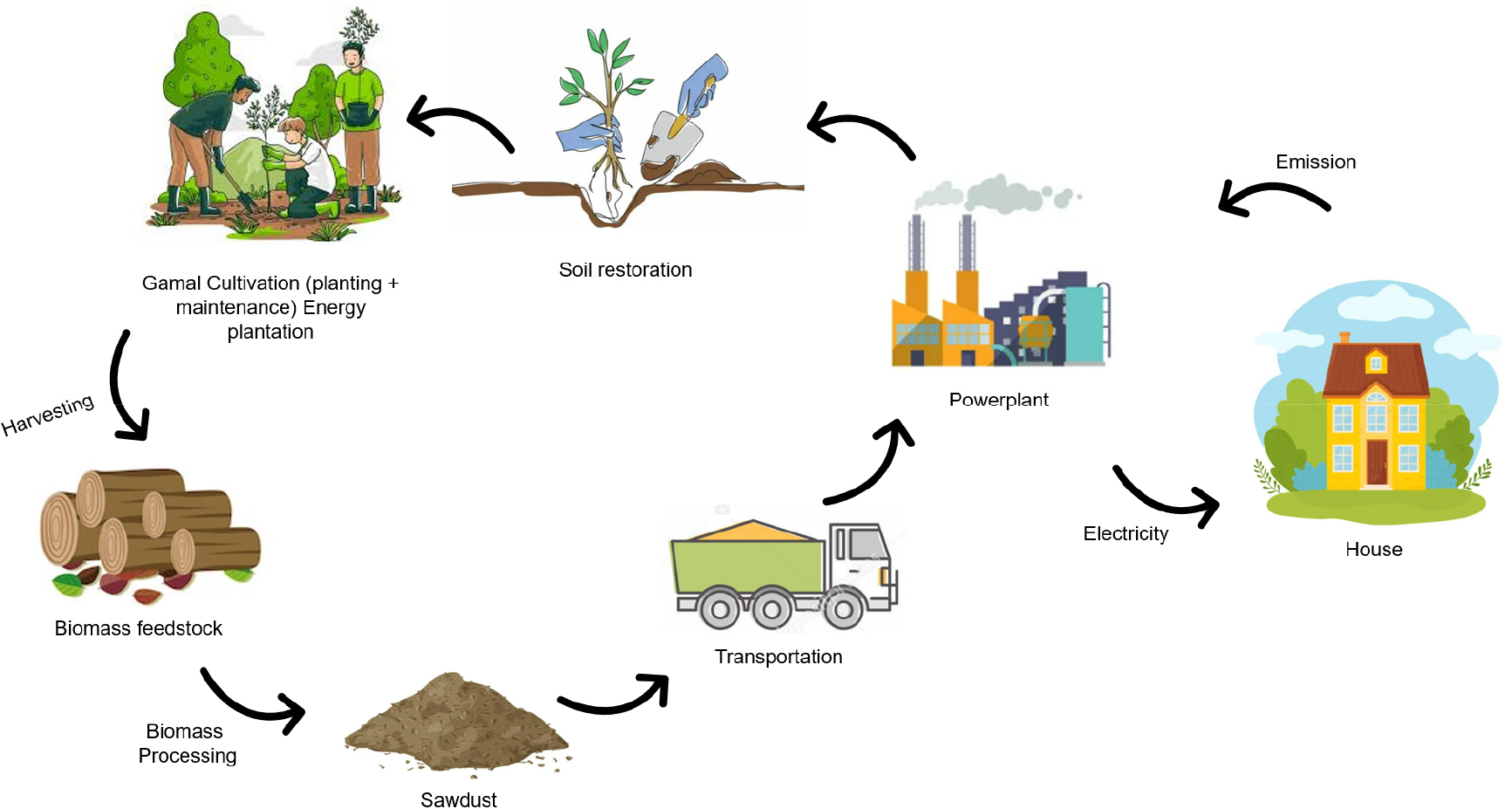
- Biomass is one of the most promising alternative energy sources. Renewable energy from biomass is generated through cultivation and processing. Conducting a …
- Biomass is one of the most promising alternative energy sources. Renewable energy from biomass is generated through cultivation and processing. Conducting a life cycle assessment (LCA) is essential to quantify the overall emissions associated with biomass energy. In Indonesia, biomass cofiring technology represents a viable option for achieving renewable energy mix targets due to its rapid implementation and low cost. The country aims to utilize 10 million tonnes of biomass annually for cofiring. This study estimates emissions from biomass used as a cofiring feedstock, derived from an integrated Gamal energy plantation forest (HTE). LCA calculations performed using SimaPro software indicate that CO2 emissions from biomass sawdust with a particle size of 2.5–3 mm amount to 222 g CO2 eq/kWh and 298 g CO2 eq/kg. In comparison, emissions from coal-based energy are three to four times higher. To accelerate a just energy transition, the Indonesian government has introduced a carbon tax of 30,000 IDR per tonne of CO2 eq in the power generation sector. However, this rate is insufficient to effectively incentivize power plants to transition from coal to biomass cofiring. A sensitivity analysis suggests that a more effective carbon tax would be at least 6.5 USD per tonne of CO2 eq. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
- Comparative Analysis of Fiber Characteristics on Recycling Potential and Paper Properties of Milk Cartons and PE-Coated Cardboard
- Yong-Hun Lee, Chul-Hwan Kim, Hyeong-Hun Park, Tae-Gyeong Lee, Ju-Hyun Park, Min-Sik Park, Jae-Sang Lee
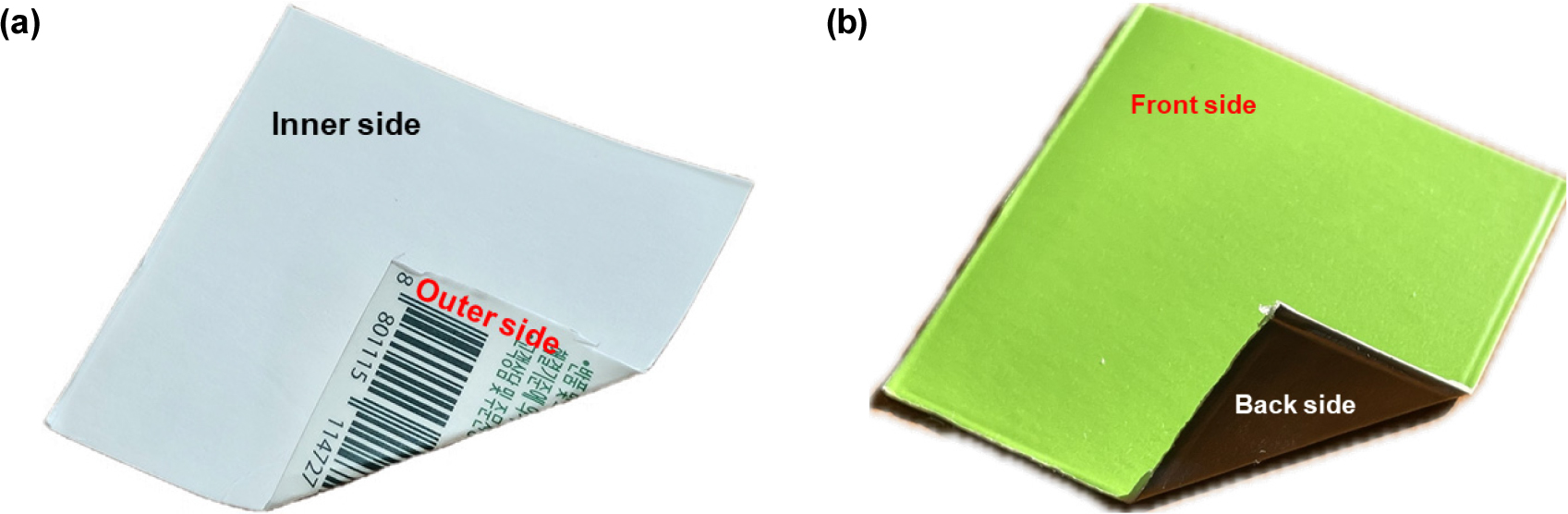
- This study examines the fiber characteristics and resultant paper properties of disintegrated milk cartons and polyethylene (PE)-coated cardboard to assess their recycling …
- This study examines the fiber characteristics and resultant paper properties of disintegrated milk cartons and polyethylene (PE)-coated cardboard to assess their recycling potential. Key differences were observed in the fiber length, fines content, and coarseness of the cartons and cardboard. The milk cartons exhibited longer and coarser fibers, whereas the PE-coated cardboard had shorter fibers and lower coarseness. The paper made from milk cartons exhibited higher freeness, lower bulk, higher tear strength, and enhanced brightness compared to those of the paper made from the cardboard, making it ideal for durable, high-clarity applications. In contrast, the PE-coated cardboard yielded paper with a higher tensile strength and bulk, aligning with the need for flexible and opaque materials. These findings underscore the necessity of understanding fiber properties to optimize recycling strategies and tailor paper products to advance the sustainability and functionality of recycled materials. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper

- Effect of Gas-Grafting Pretreatment of Cellulose on Properties of Cellulose-Polypropylene Composites
- Kyu Hwan Noh, Kyoung-Hwa Choi, Kwang-Seob Lee, Philippe Martinez, Jeong-Yong Ryu
- This study investigated a new gas grafting method using palmitoyl chloride to enhance the hydrophobicity of cellulose fiber sheets and their blending …
- This study investigated a new gas grafting method using palmitoyl chloride to enhance the hydrophobicity of cellulose fiber sheets and their blending compatibility with polypropylene. In addition, cellulose fiber sheets were produced by substituting ethanol for water in the fiber stock during sheet molding to prevent macrofibril matting on the fiber surface, thereby improving the hydrophobization efficiency achieved by gas grafting. Results revealed that alcohol-molded sheets exhibited more than twice the amount of reacted palmitoyl chloride compared to conventional water-based fiber sheets after gas grafting. Composite films made from pretreated fibers exhibited higher tensile strength than those made from un-grafted fibers. The addition of maleic anhydride polypropylene reduced fiber agglomeration and ultimately improved dispersion by decreasing the melt flow index (MFI) of the composites. However, the use of hydrophobized fibers in polypropylene composites—via gas grafting of the fiber sheets—increased the MFI due to enhanced fiber dispersibility. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
-
A Study on the Carbonization Characteristics of Citrus Pomace for Biochar Production
감귤박 바이오차 제조를 위한 감귤박 탄화특성 연구
-
Myeong Ho Lee, Su In Cho, Soon Hwa Kwon, Yong Joo Sung
이명호, 조수인, 권순화, 성용주
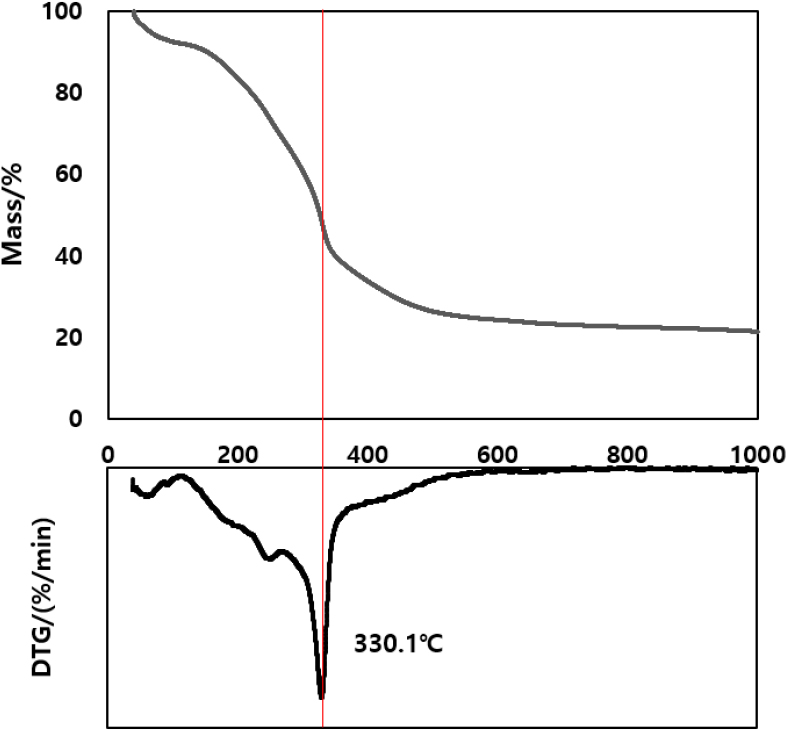
- This study investigated the pyrolytic conversion of citrus pomace into biochar, aiming to establish optimal conditions for its production and evaluate its …
- This study investigated the pyrolytic conversion of citrus pomace into biochar, aiming to establish optimal conditions for its production and evaluate its physico-chemical properties. Carbonization was conducted at temperatures ranging from 350 to 550°C and residence times varying from 10 to 120 min. The effects of carbonization conditions on biochar yield, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and elemental composition ratios were systematically investigated. Results revealed that increasing the carbonization temperature and residence time decreased the biochar yield but increased the biochar pH and carbon (C) content. Elemental analysis revealed that as carbonization progressed, the C content increased while the hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) contents decreased, lowering the H/C and O/C molar ratios. To address the inherently low yield and quality of citrus-pomace-derived biochar, co-pyrolysis with lignin-rich fallen leaves was explored. Increasing the proportion of fallen leaves enhanced the overall biochar yield while reducing the pH and EC of the resulting biochar. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Carbonization Characteristics of Citrus Pomace for Biochar Production



 Journal of Korea TAPPI
Journal of Korea TAPPI







