-
Review
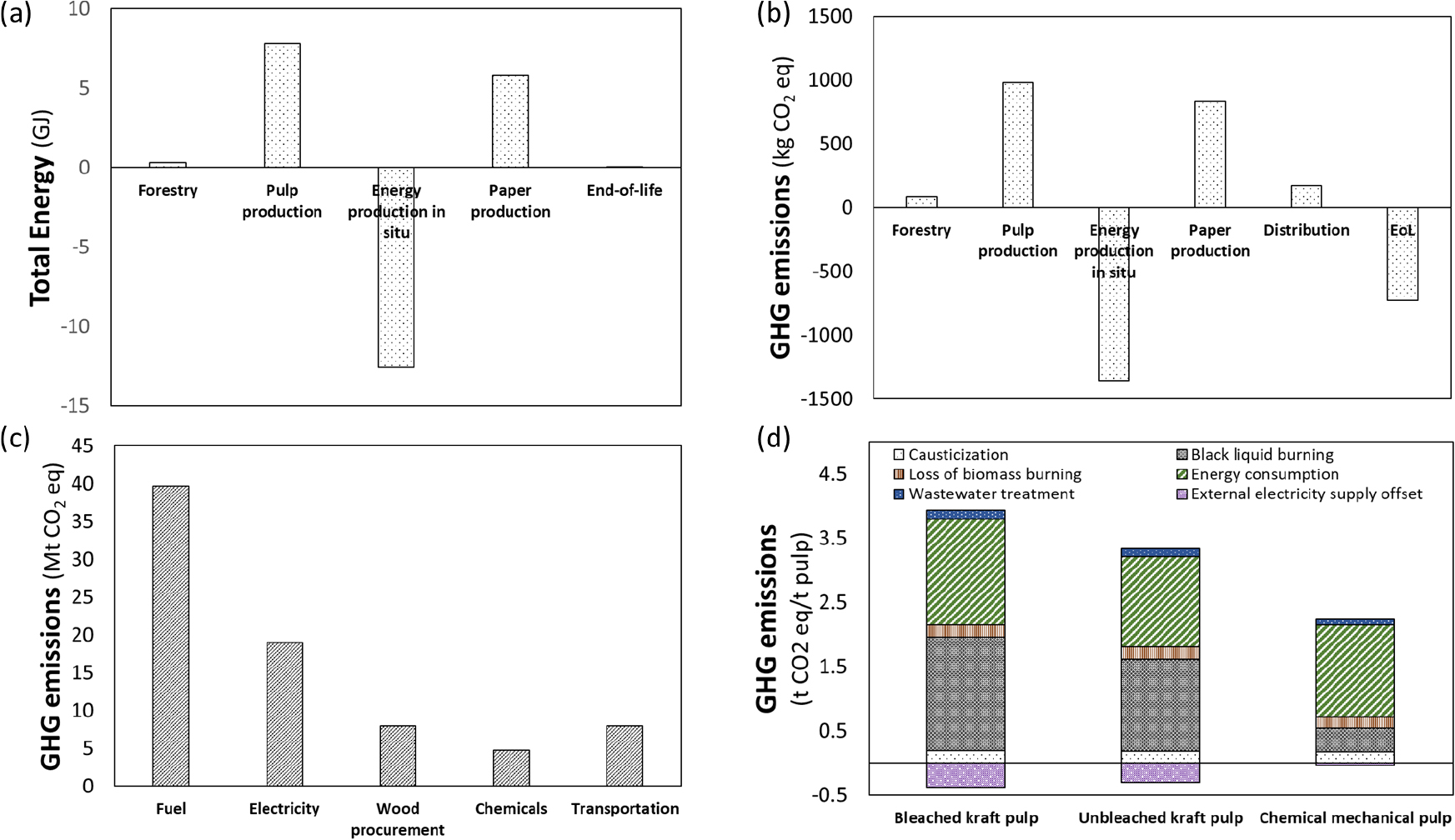
- Recent Trends in Life Cycle Assessment Studies on Pulp- and Paper-Based Materials
- Seokmin Hong, Junhyeok Park, Semin Kang, Kyudeok Oh, Soojin Kwon
- The pulp and paper sector is both highly energy- and resource-intensive. However, it remains a key supplier of renewable and recyclable materials …
- The pulp and paper sector is both highly energy- and resource-intensive. However, it remains a key supplier of renewable and recyclable materials in the transition away from fossil-based products. This review synthesizes approximately two decades of life cycle assessment (LCA) studies on pulp- and paper-based materials, with emphasis on research published from approximately 2003 to 2025. The literature is first mapped in terms of processes and products covered, system boundaries, functional units, and regional focus, revealing a strong concentration on mass-based functional units, European and Asian case studies, and attributional LCAs that prioritize climate- and energy-related indicators. Mill- and sector-level case studies consistently identify pulping, bleaching, and drying, as well as associated steam and electricity generation, as dominant contributors to global warming potential and other midpoint impacts. Additionally, they highlight the dual role of kraft mills as both major energy consumers and producers of biomass-based heat and power. Comparative LCAs further evaluate how recycling strategies, end-of-life options, alternative fibers, and paper-based packaging systems perform relative to virgin routes and nonpaper competitors, showing that environmental benefits are highly context-dependent and sensitive to background energy mixes, fiber-yield assumptions, and market-mediated effects. Overall, this review highlights that robust decarbonization and circularity strategies for the pulp and paper sector will require context-specific sets of measures, such as energy-efficiency improvements, fuel switching toward low-carbon and biomass-based energy, optimized waste and wastewater management, and more efficient fiber use, all supported by more consistent, dynamic, and decision-oriented LCA practice. - COLLAPSE
-
Review
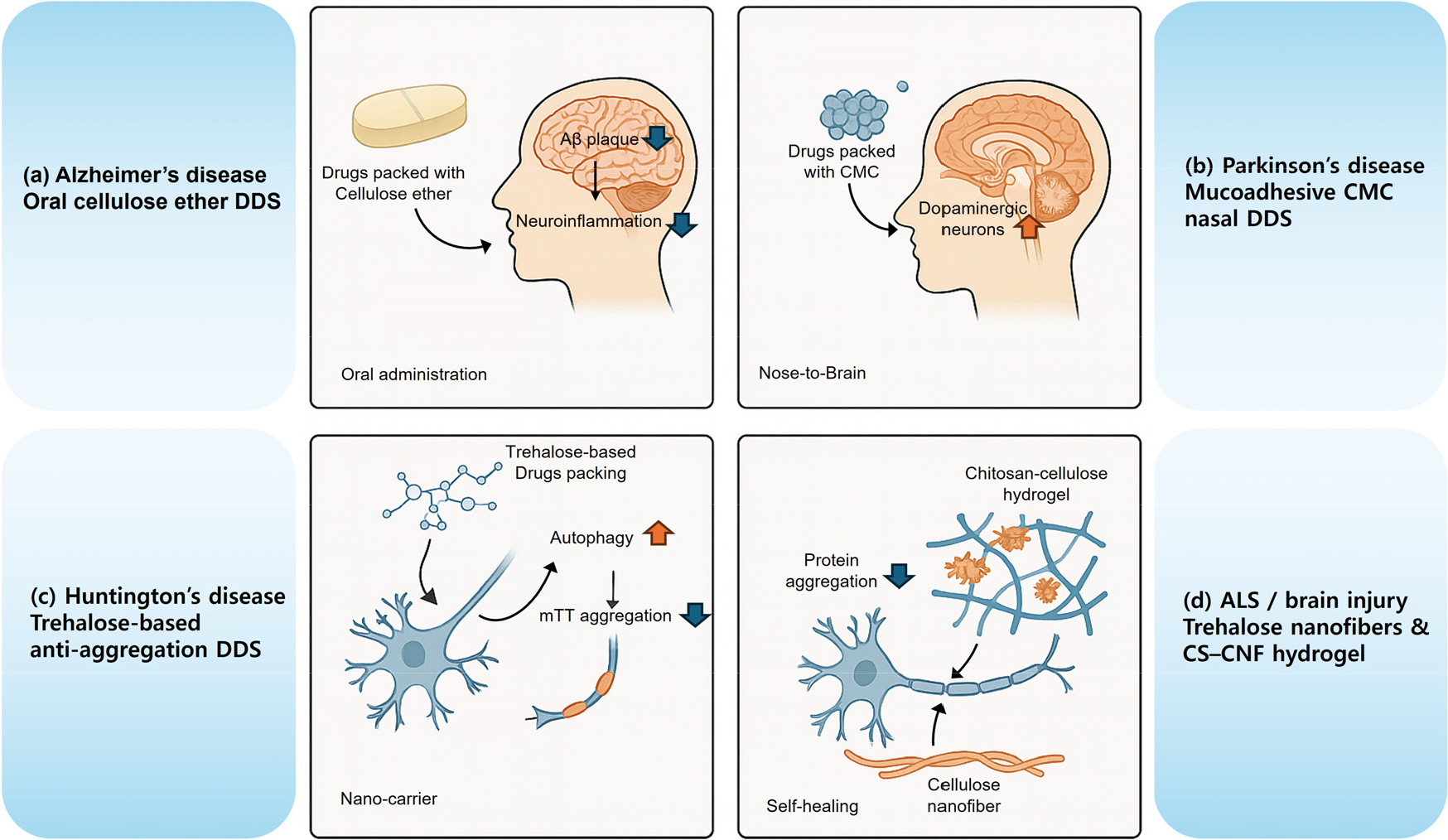
-
Applications and Design Strategies of Cellulose-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
퇴행성뇌질환 치료를 위한 셀룰로오스 기반 약물전달시스템의 응용과 설계전략
-
Hanwoong Woo, Jin Ho Seo, Jieun Kim
우한웅, 서진호, 김지은
- Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are characterized by a progressive loss of neurons driven by protein …
- Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are characterized by a progressive loss of neurons driven by protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. Additionally, the blood–brain barrier (BBB) severely restricts the delivery of most therapeutics to the brain. In this context, cellulose and nanocellulose have emerged as sustainable drug delivery systems (DDSs) owing to their renewable biomass-based origin, excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability, high mechanical strength, and abundant surface hydroxyl groups that enable versatile chemical functionalization. This review summarizes the structural and physicochemical properties of bulk, nanocrystal, nanofibril, and bacterial celluloses that are crucial for designing DDSs that can target the brain. These include a high specific surface area, as well as tunable network formation, surface charge, and hydrophilicity. The review highlights representative preclinical applications in major neurodegenerative diseases, such as cellulose ether-based oral formulations that modulate amyloid-β pathology, mucoadhesive carboxymethyl cellulose nasal nanocrystals for nose-to-brain delivery of dopaminergic agents, trehalose–cellulose systems targeting mutant huntingtin aggregation, and chitosan–nanocellulose hydrogels that support neural tissue repair. Finally, it critically discusses the current relevance and limitations of cellulose-based DDSs compared with liposomal and polymeric nanoparticles and outlines future design strategies involving advanced surface functionalization, hybrid and multilayer architectures, integration with neural tissue engineering, and processes for regulatory standardization to enable clinical translation in neurodegenerative disease therapy. - COLLAPSE
-
Applications and Design Strategies of Cellulose-Based Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
-
Original Paper
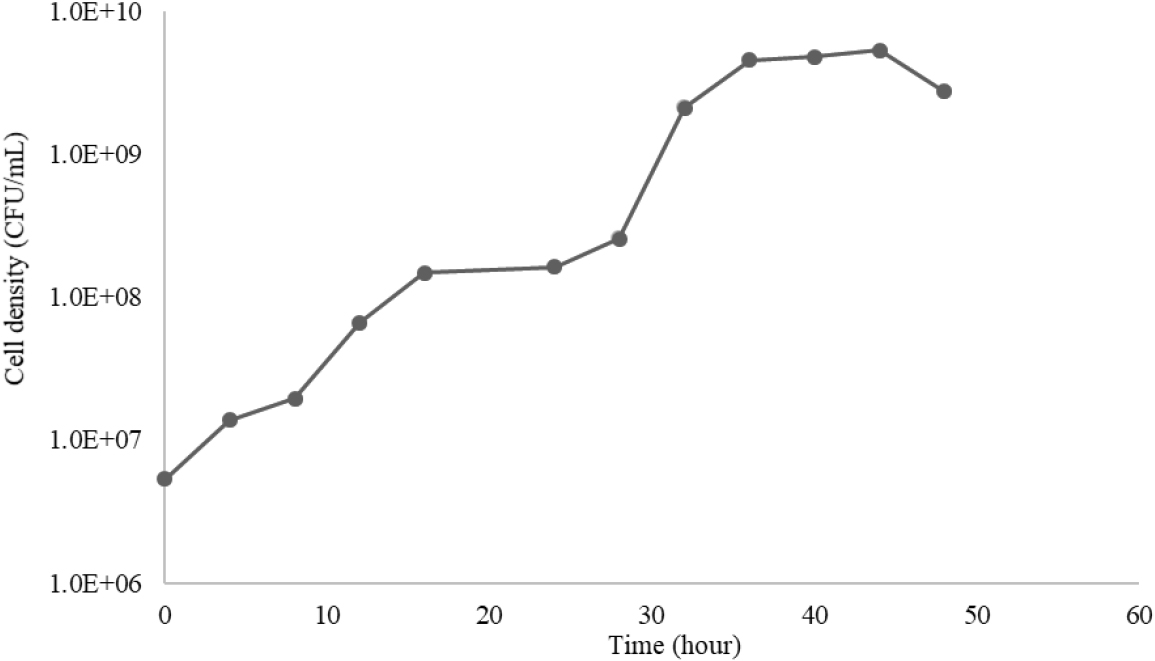
- Optimization of Bacterial Nanocellulose Production from Sweet Potato Waste via Response Surface Methodology
- Lili Melani, Grace Brigitta Gunawan, Reso Aji Saputra Wicaksono, Gilang Mahendra Pratama
- Cilembu sweet potato is a high-yielding Indonesian variety that generates considerable agro-industrial waste from unconsumed biomass. Owing to its high carbohydrate content, …
- Cilembu sweet potato is a high-yielding Indonesian variety that generates considerable agro-industrial waste from unconsumed biomass. Owing to its high carbohydrate content, this waste hydrolysate was evaluated as a carbon source for the cultivation of Gluconacetobacter xylinus to produce bacterial nanocellulose (BNC). Production parameters were optimized using a Box–Behnken experimental design to assess the effects of initial pH, bacterial inoculum volume, and D-glucose concentration on BNC yield. Statistical analysis indicated that both pH and inoculum concentration significantly influenced yield, whereas D-glucose concentration had no statistically significant effect (p = 0.059). Optimal conditions were identified at pH 5.7 and 10% inoculum, yielding 3.97 g/L of BNC. The synthesized BNC consisted of interconnected nanofibers of 10–100 nm in diameter, with a crystallinity index of up to 77%. Collectively, these results demonstrate that Cilembu sweet potato waste hydrolysate represents an efficient and sustainable carbon substrate for BNC biosynthesis, eliminating the need for additional glucose supplementation. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
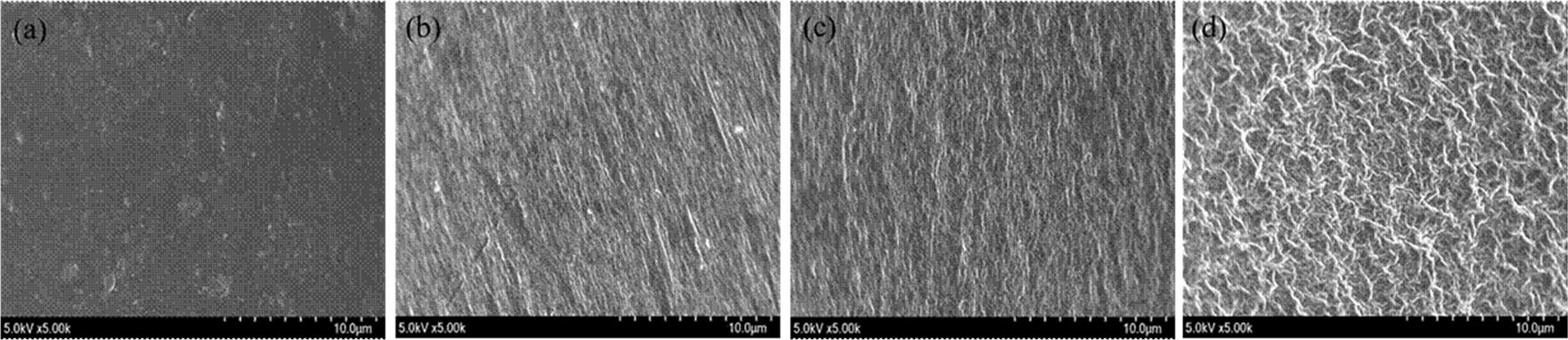
- Preparation and Characterization of Methyl Cellulose/Pullulan/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite Film for Packaging Applications
- Jungeon Lee, Jae Hoon Jung, Sabina Yeasmin, Neul-Sae-Rom Kim, Seong Baek Yang, Dong-Jun Kwon, Jung Wan Kim, Jeong Hyun Yeum
- Methyl cellulose (MC) and pullulan (PULL) blend films with varying ratios were fabricated, with the MC/PULL 60/40 composition exhibiting the best mechanical …
- Methyl cellulose (MC) and pullulan (PULL) blend films with varying ratios were fabricated, with the MC/PULL 60/40 composition exhibiting the best mechanical performance. Montmorillonite (MMT) was incorporated (1–5 wt.%) into the 60/40 matrix to further enhance the film properties. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the complete exfoliation and uniform dispersion of MMT platelets, indicating strong miscibility within the polymer matrix. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy revealed strong interactions among MC, PULL, and MMT. Thermogravimetric analysis demonstrated that the temperature corresponding to 50% decomposition increased with MMT loading of up to 3% but decreased at 5%. Water contact angle measurements indicated an increase in hydrophobicity with rising MMT content (from 61.4° to 64.4°). These environmentally friendly nanocomposite films exhibit enhanced mechanical, thermal, and surface properties while maintaining biodegradability, making them promising candidates for sustainable food packaging and protective applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
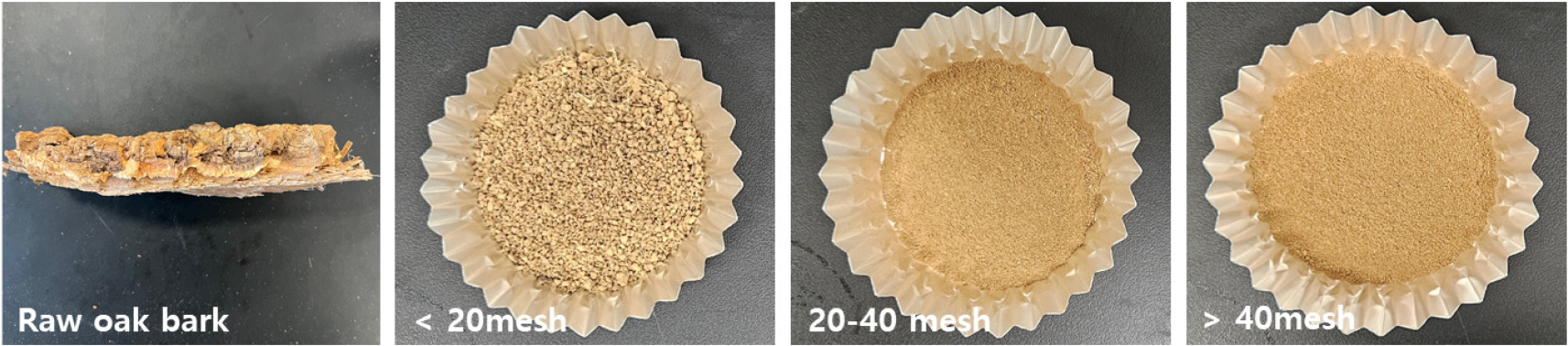
- Study on the Valorization of Oak Bark Biomass - Part I: Extraction and Characterization of Tannins
- Sa Rang Choi, Jung Myoung Lee
- Oak bark, an abundant but underutilized biomass, is often combusted as fuel or discarded. This study aims to valorize this biomass by …
- Oak bark, an abundant but underutilized biomass, is often combusted as fuel or discarded. This study aims to valorize this biomass by efficiently extracting tannins, a class of natural polyphenolic compounds. The effects of bark particle size, solvent type, and solvent concentration on the extraction yield and tannin composition were evaluated. The highest extraction yield (6.3%) was obtained from bark particles with a size range of 20–40 mesh. Despite their slightly lower extraction yields, finer particles (> 40 mesh) exhibited higher total polyphenol and tannin contents. Among the solvents tested, 90% ethanol provided the highest average yield (6.4%), whereas acetone resulted in lower yields but higher tannin purity. The recovery efficiency of condensed tannins was maximized when bark particles > 40 mesh were extracted using 90% ethanol. These findings demonstrate the crucial roles of particle size and solvent selection in determining the quantitative and qualitative efficiency of tannin extraction, confirming the potential of oak bark as a valuable biobased resource. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
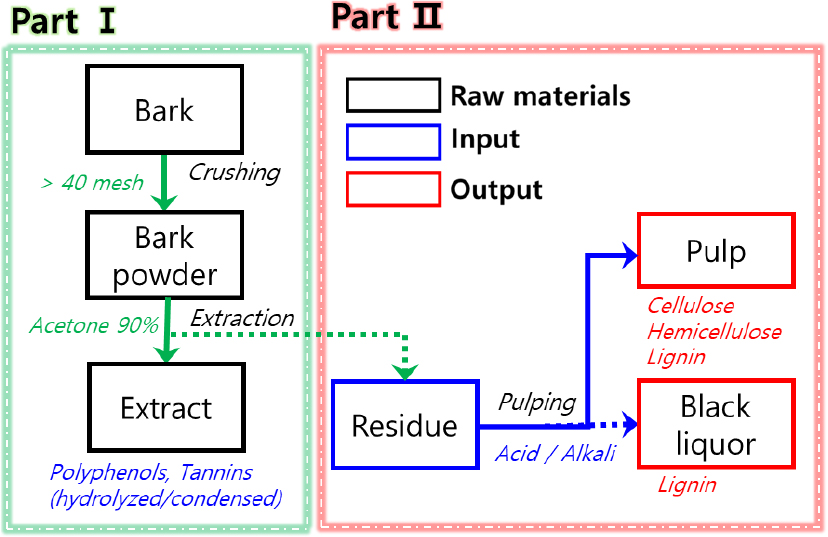
- Study on the Valorization of Oak Bark Biomass - Part II: Organosolv Pulping of Bark Residue after Tannin Extraction
- Sa Rang Choi, Jung Myoung Lee
- Bark, a significant byproduct of the wood industry accounting for 10–20% of log weight, is typically utilized for low-value applications because of …
- Bark, a significant byproduct of the wood industry accounting for 10–20% of log weight, is typically utilized for low-value applications because of its high ash and lignin contents. Nevertheless, it remains a rich source of cellulose and hemicellulose, offering potential as a high-value bioproduct feedstock through appropriate pretreatment and pulping. In this study, tannin-extracted oak bark residues were subjected to organosolv pulping using either acidic (H2SO4) or alkaline (NaOH) catalysts. The pulp yields were 39.4% and 45.6% under Acid 60 (120°C, 60 min) and Alkali 90 (120°C, 90 min) conditions, respectively. Acidic pulping induced partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides, whereas alkaline treatment facilitated lignin–hemicellulose cleavage and improved carbohydrate preservation. Lignin recovered from black liquor under Acid 60 conditions exhibited the highest purity (82.8%) and recovery yield (37.3%). The resulting pulps were directly micronized by homogenization to produce well-dispersed microfibers without additional pretreatment. Overall, these findings demonstrate that tannin-extracted bark residues are promising precursors for microfibers suitable as bio-based fillers and compatibilizers, contributing to the sustainable valorization of underutilized forest biomass. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
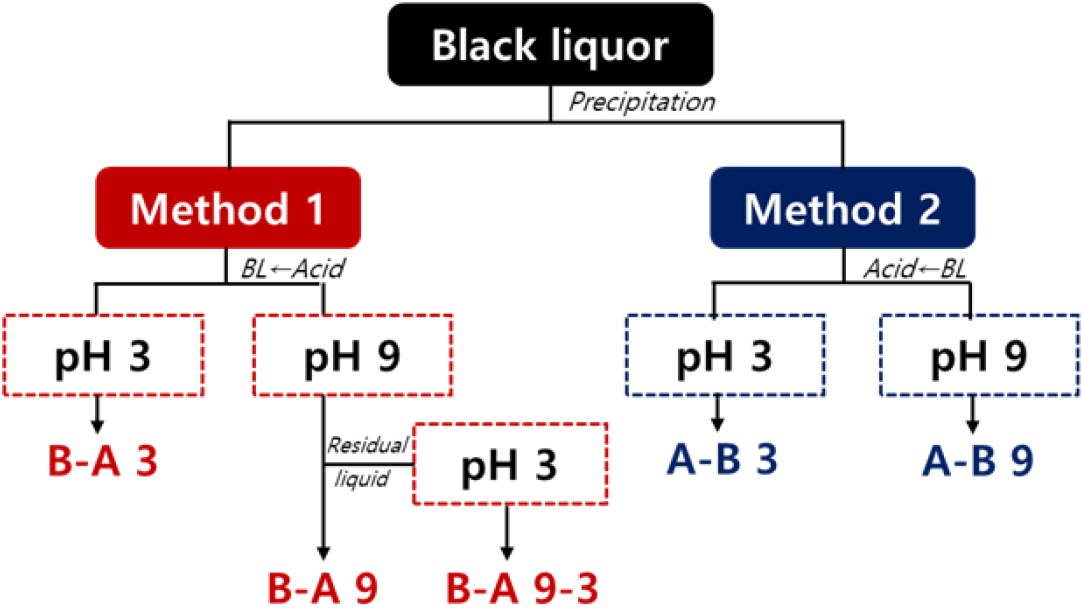
- Effect of Lignin Recovery Conditions from Hardwood Kraft Black Liquor on Lignin Characteristics
- Sa Rang Choi, Eon Jin Park, Jung Myoung Lee
- Black liquor, generated during the pulp and paper manufacturing process, is produced in millions of tons annually; however, most of it is …
- Black liquor, generated during the pulp and paper manufacturing process, is produced in millions of tons annually; however, most of it is burned as boiler fuel for energy recovery. Recently, efforts have increasingly been made to utilize this low-value byproduct as a source of functional industrial materials by converting the lignin it contains into high-performance biopolymers. In this study, lignin was recovered from hardwood kraft black liquor, and the effects of acid addition sequence, precipitation pH, and black liquor dilution ratio on recovery efficiency and lignin characteristics were systematically analyzed. The highest lignin recovery was achieved under single acidification at pH 3, while the recovery method based on adding black liquor to acid exhibited slightly higher recovery efficiency than that based on adding acid to black liquor. Molecular weight analysis revealed that under strongly acidic conditions, Mw decreased and a lower polydispersity index (PDI) was achieved, indicating a more uniform molecular weight distribution. Additionally, experiments on dilution concentration showed that lignin with the highest purity (up to 94.7%) and the most homogeneous molecular structure was obtained at 20% dilution. These results demonstrate that lignin fractionation and structural control can be achieved through precise adjustment of acidification and dilution conditions, providing a strong foundation for optimizing process strategies in the development of lignin-based functional polymer materials. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
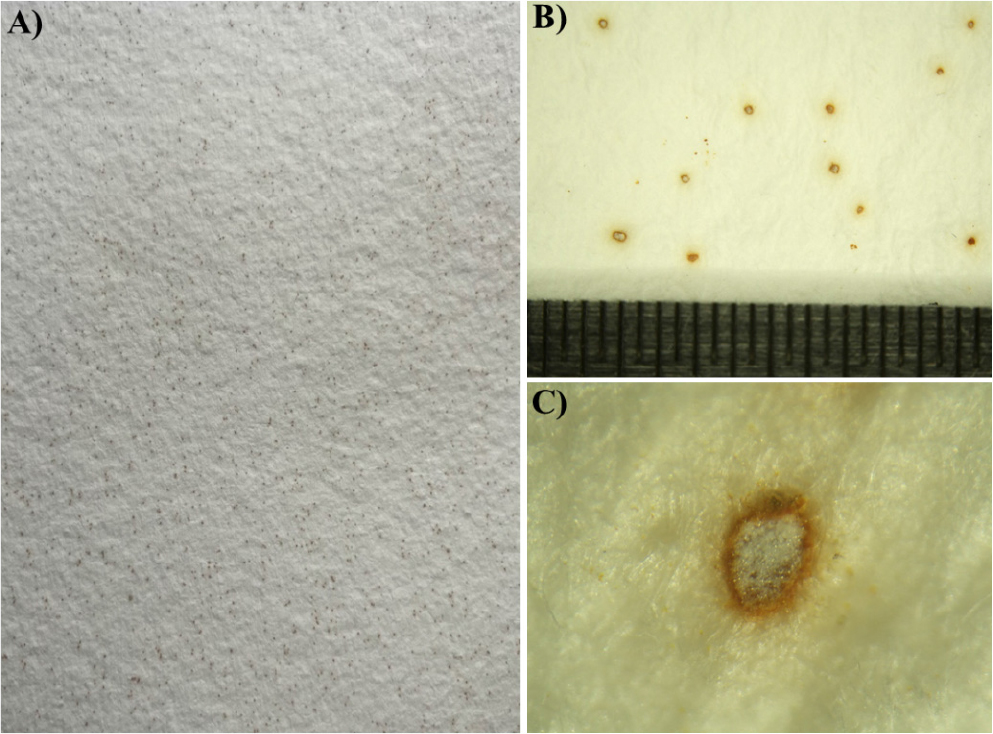
- The First Record of Cleistothecial Thermoascus crustaceus isolated from Dried Hardwood Pulp in Korea
- Sunirmal Sheet, Marma Mamaching, Yang Soo Lee
- Radish-brown spots of fungal contamination was detected on dried hardwood pulp sheets during storage at a paper manufacturing company in Korea. Therefore, …
- Radish-brown spots of fungal contamination was detected on dried hardwood pulp sheets during storage at a paper manufacturing company in Korea. Therefore, this study was conducted to identify and characterize the fungal contaminant responsible for the discoloration observed in the stored hardwood pulp sheets. A new thermophilic cleistothecial fungal isolate recovered from these affected regions was identified as Thermoascus crustaceus by sequencing of the partial D1–D2 region of the long rRNA gene, which exhibited 100% identity with the reference strains JF922031.1, FJ358289.1, and EU021597.1. Morphological analyses by light microscopy revealed prolific conidial clusters and extensive hyphal networks colonizing the discolored hardwood pulp surfaces. The isolate demonstrated optimal growth at 50°C, consistent with adaptation to the high processing temperatures used during papermaking. This study reports the first documented isolation of T. crustaceus related to fungal contamination and discoloration in hardwood pulp sheets from Korea and emphasizes the ecological and industrial significance of thermophilic Ascomycota in high-temperature manufacturing environments. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Paper
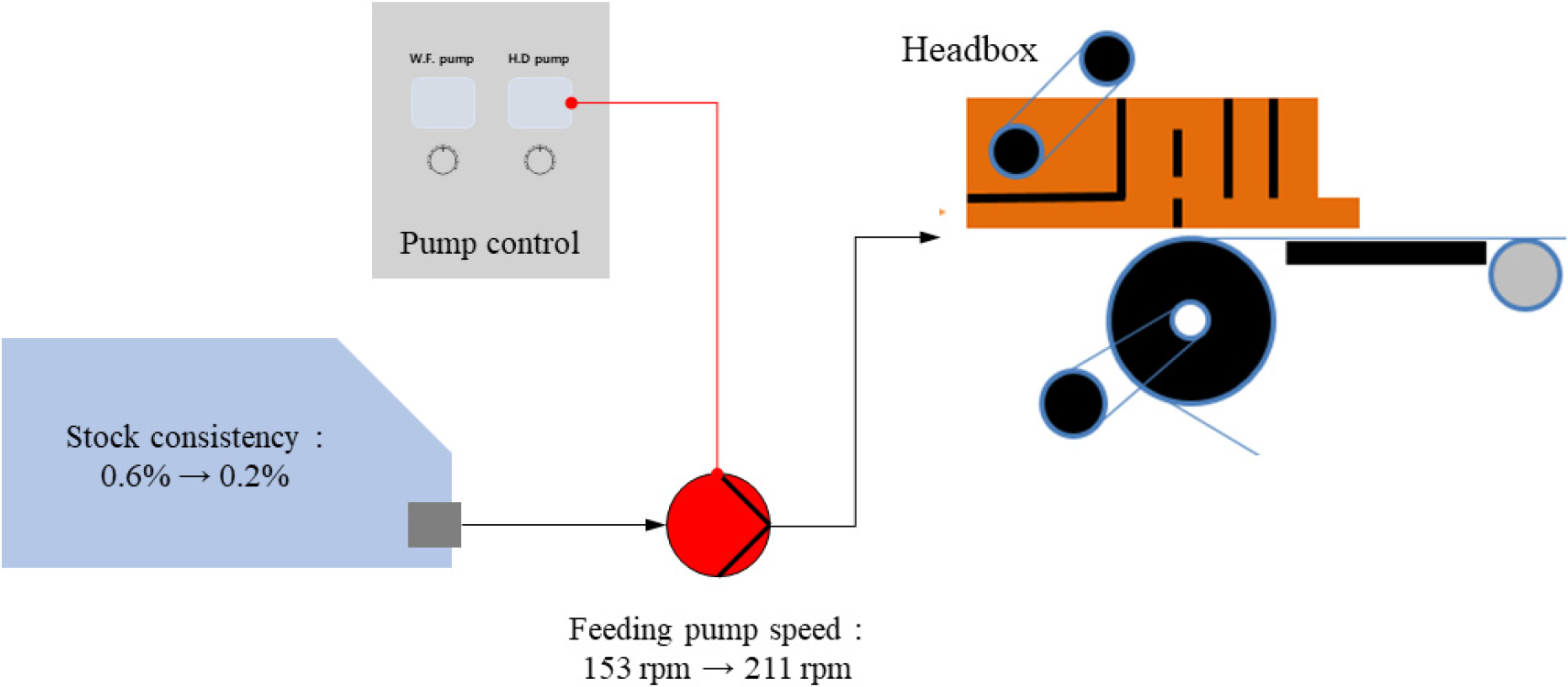
-
Analysis of Fiber Orientation of Paper Using Pilot Machine with Open Headbox (3) - Effect of Stock Concentration and Feeding Speed
오픈 헤드박스형 파일럿 초지기의 섬유 배향 분석(3) - 지료 농도 및 사출 속도에 따른 영향
-
Kyoung-Hwa Choi, Kwang Seob Lee, Jeong-Yong Ryu
최경화, 이광섭, 류정용
- This study investigated the potential to improve fiber orientation in paper by controlling stock concentration and feed speed during papermaking, using a …
- This study investigated the potential to improve fiber orientation in paper by controlling stock concentration and feed speed during papermaking, using a pilot-scale wet-web forming machine equipped with an open-type headbox. To regulate jet velocity at the slice outlet of the headbox, stock concentration was varied, and the pumping speed of the stock supply was adjusted accordingly. Paper sheets were then fabricated under each condition, and their physical properties, including grammage, formation, and tensile strength in both the machine direction (MD) and cross direction (CD), were quantified and compared. The results revealed that increasing both stock concentration and jet velocity raised grammage and thickness by increasing the amount of stock delivered per unit area of the wire, thereby enhancing sheet-forming capacity. At higher stock concentrations, faster consolidation reduced fiber non-uniformity in the CD, which led to a notable increase in tensile strength in the CD and, consequently, a higher CD/MD tensile index ratio. Furthermore, higher jet velocity intensified turbulence from the stock’s impact on the turbulence plate in the headbox, which suppressed excessive fiber alignment in the MD and further improved CD tensile strength. These findings demonstrate that appropriate control of stock concentration and jet velocity during the forming process can effectively regulate fiber orientation and improve sheet uniformity inpapermaking. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Fiber Orientation of Paper Using Pilot Machine with Open Headbox (3) - Effect of Stock Concentration and Feeding Speed
-
Original Paper
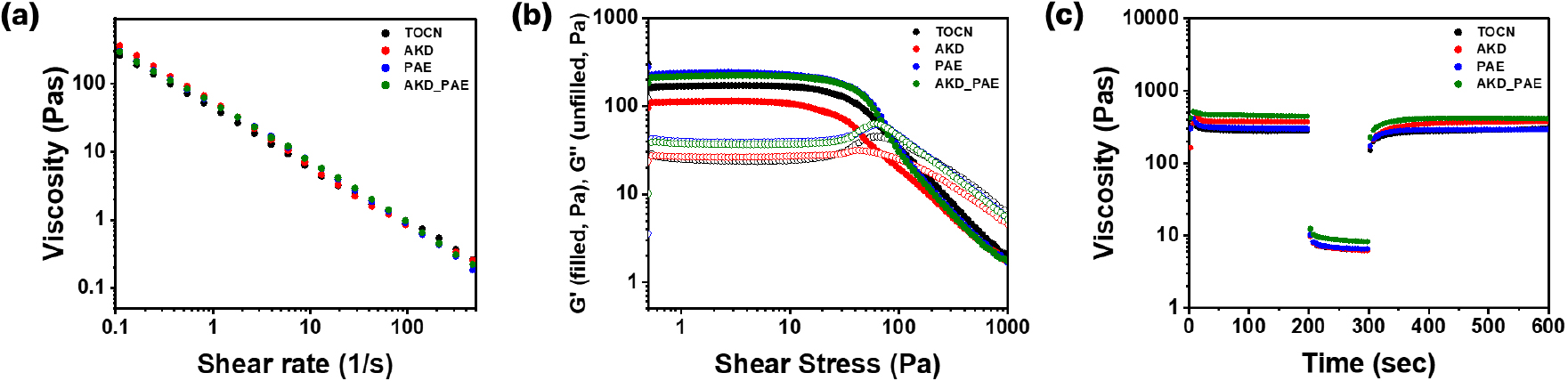
-
Enhancement of Barrier Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Coated Paper via AKD and PAE Incorporation
AKD 및 PAE 복합화를 통한 나노셀룰로오스 기반 코팅지의 차단성 향상
-
Soyoung Chae, Hakmyoung Lee, Hyein Kim, Seung-wook Park, Seongmin Yoo, Kunhee Lee, Hye Jung Youn
채소영, 이학명, 김혜인, 박승욱, 유성민, 이건희, 윤혜정
- Environmental concerns associated with conventional plastic packaging have increased the demand for eco-friendly alternatives. Paper, a biodegradable and recyclable material, is a …
- Environmental concerns associated with conventional plastic packaging have increased the demand for eco-friendly alternatives. Paper, a biodegradable and recyclable material, is a promising substitute; however, its porous and hydrophilic nature limits its barrier performance. To overcome these limitations, this study employed TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils (TOCNs) as the primary barrier-coating material. Alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) and polyamideamine epichlorohydrin (PAE) were incorporated as hydrophobizing and cross-linking agents, respectively. The rheological properties of the TOCN-based coating solutions and the resulting coated papers were evaluated through Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, water and gas barrier measurements, and mechanical testing. AKD increased hydrophobicity and reduced surface moisture adsorption, whereas PAE enhanced network stability through cross-linking. Their combined addition produced a higher water contact angle and improved water vapor transmission resistance and wet tensile strength. These results indicate that conventional papermaking additives can effectively enhance the barrier properties and structural stability of nanocellulose-based coatings, supporting their potential for high-performance, eco-friendly paper packaging applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Enhancement of Barrier Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Coated Paper via AKD and PAE Incorporation
-
Original Paper
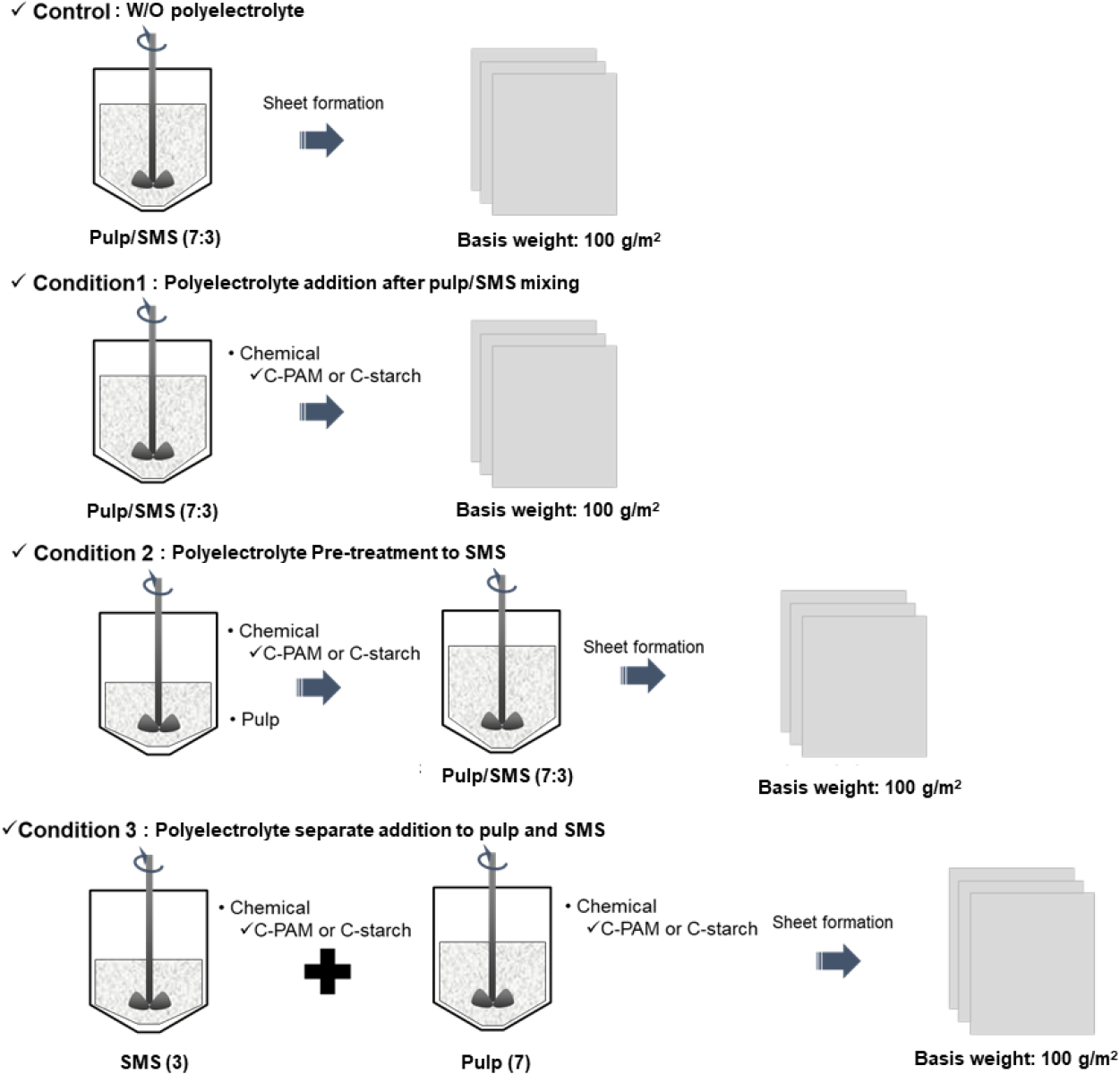
-
Enhancement of Mechanical and Surface Properties of Composite Sheets Prepared Using Spent Mushroom Substrate
버섯 폐배지를 활용한 복합시트의 강도 및 표면 특성 향상
-
Seungmin Han, Yoon-hyuck Choi, Wanhee Im, Jae-Hun Jung, Cho-Hyun Jeon, Jiyeon Oh, Sangsu Lee
한승민, 최윤혁, 임완희, 정재훈, 전초현, 오지연, 이상수
- Herein, composite sheets were fabricated using wood pulp and spent mushroom substrate (SMS). The effects of cationic polyelectrolytes, such as cationic polyacrylamide …
- Herein, composite sheets were fabricated using wood pulp and spent mushroom substrate (SMS). The effects of cationic polyelectrolytes, such as cationic polyacrylamide and cationic starch, and surface sizing on the properties of these sheets were examined. The addition amount and sequence of cationic polyelectrolytes were varied to enhance the properties of composite sheets. The tensile index of the sheets increased upon adding cationic polyelectrolytes into the pulp/SMS mixture stock compared with that under other conditions. In addition, the smoothness and tensile index of the sheets improved upon reducing the particle size of the SMS from 65 to 38 µm owing to uniform particle dispersion and enhanced fiber–particle bonding area in the composite sheets. These properties also enhanced after surface sizing under all preparation conditions. Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images confirmed that smaller SMS particles exhibited higher surface retention on the composite sheets than larger particles. - COLLAPSE
-
Enhancement of Mechanical and Surface Properties of Composite Sheets Prepared Using Spent Mushroom Substrate



 Journal of Korea TAPPI
Journal of Korea TAPPI







